|
九大景點
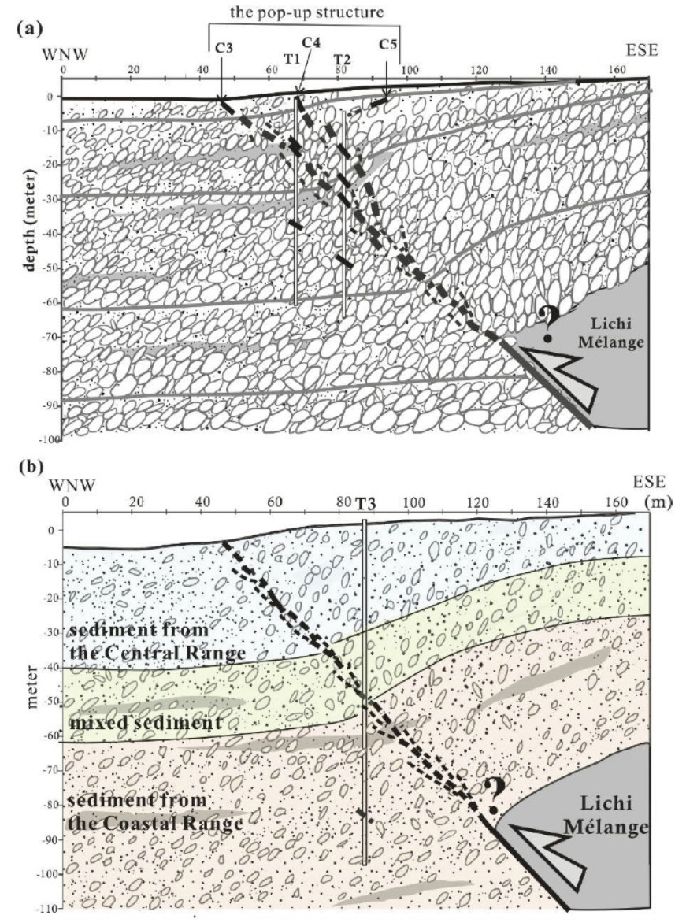
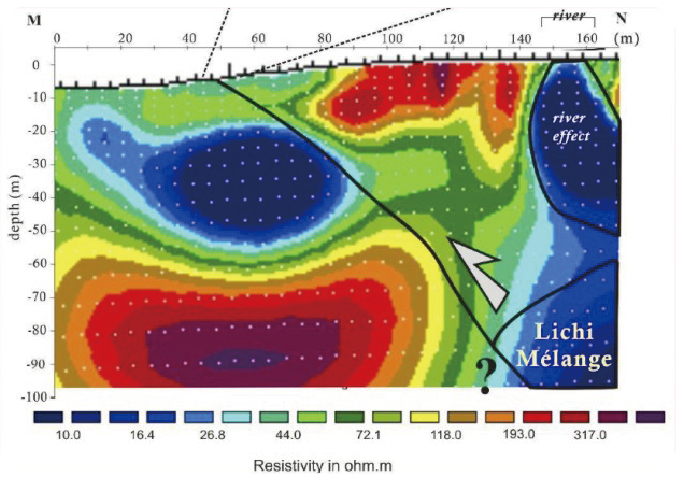
斷層現地試驗場及監測站在這裡,科學家進行了一系列的現地探測及試驗。結合地質鑽探岩心分析、槽溝開挖、震測剖面、地電阻剖面等探測,配合原先之大地變形測量(潛變儀、GPS、水準等),除了可以建構錦園沖積扇地區的地下地質與斷層構造,發現沖積扇有超過100公尺厚,而斷層在沖積扇的礫石層中發展成許多不連續的裂縫;同時推求沖積扇的沈積速率(約每年一公分)與斷層滑移造成上盤的相對抬升速率(每年將近三公分)。 地質學家也在這實驗場進行探測斷層帶水文力學的試驗及量測。跨越斷層共有5孔水文觀測井。利用大型抽注水實驗,發現到斷層帶其實是個阻水層,將上下盤水文系統隔開,雖然還是有較緩慢交流。另外定期持續的水位監測及微水試驗,也幫助獲得地下水層滲透系數及其變化。 On-site Experiments in Fault ZoneThis site is located across the geomorphic scarp of the Chihshang Fault with little disturbance of human construction. Scientists take this advantage to use here as an experiment site, to conduct different investigations. The investigations include borehole drilling and analysis, trench excavation, seismic reflection, and electric resistivity profiles, which allow reconstructing the shallow structures and fault architecture in the Chinyuan alluvial fan. One then discovered that the thickness of the deposits of the fan is more than 100 m and that the Chihshang Fault has developed numerous discontinuous fractures within the covered unconsolidated gravels. Geologists also obtained a sedimentation rate of about 1 cm per year of the fan and the relative uplift rate of 3 cm per year in the hanging wall with respect to the footwall. Geohydrologists also conducted several hydraulic experiments at this site. Injection and pumping experiments together with on-site tiltmeters recording analyses revealed that the fault plane acts as hydraulic barrier to separate the flow systems between hanging wall and footwall. Continuous groundwater leveling monitoring and monthly pulse tests allow obtaining the permeability of the alluvial gravels in the fault zone and its evolution through time. 建構斷層地下構造Construct subsurface fault structures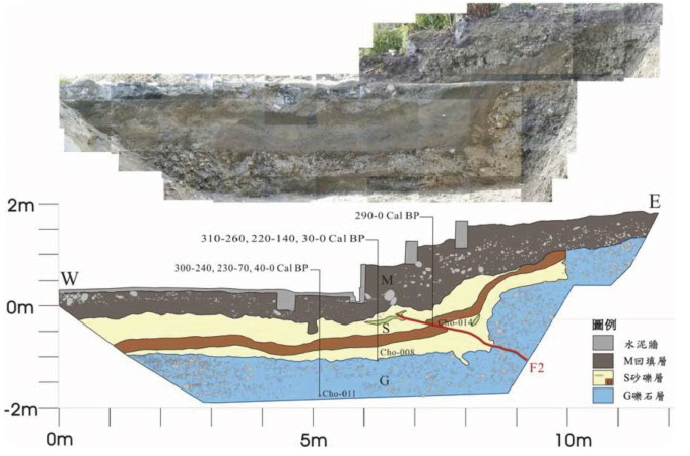
槽溝開挖
鑽井岩芯分析
水準測量
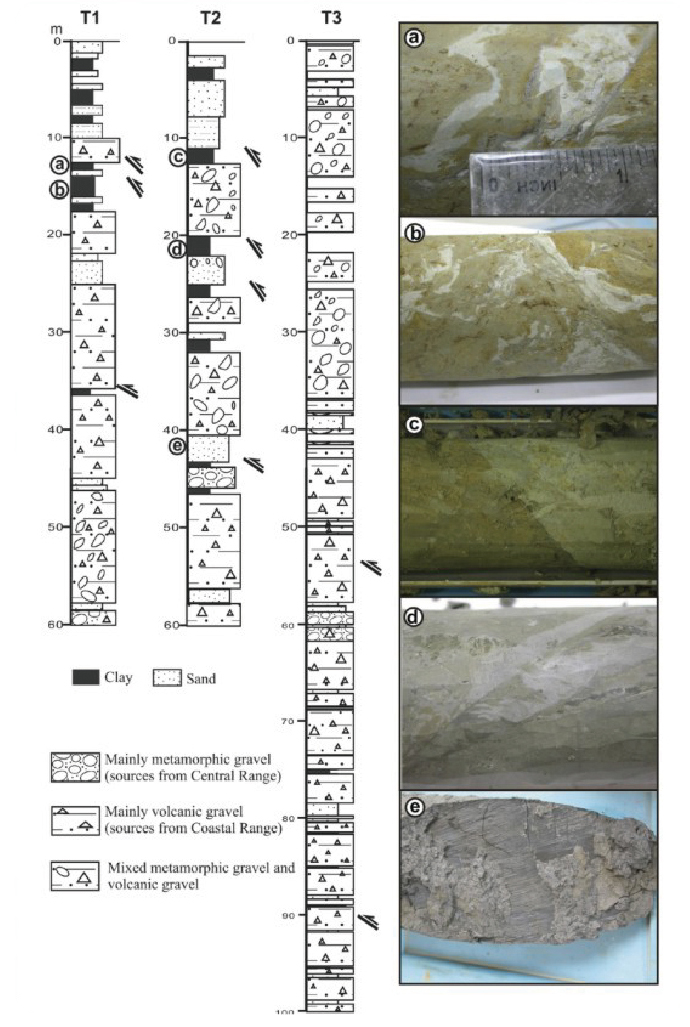
圖一、從各種現地試驗及探測建立之池上斷層淺部地下構造及斷層模型。
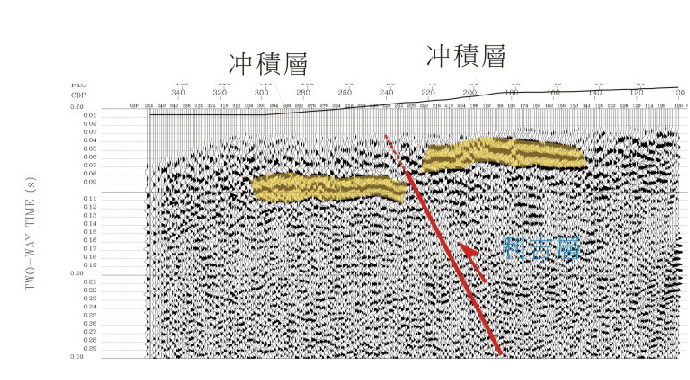
震測剖面
地電剖面
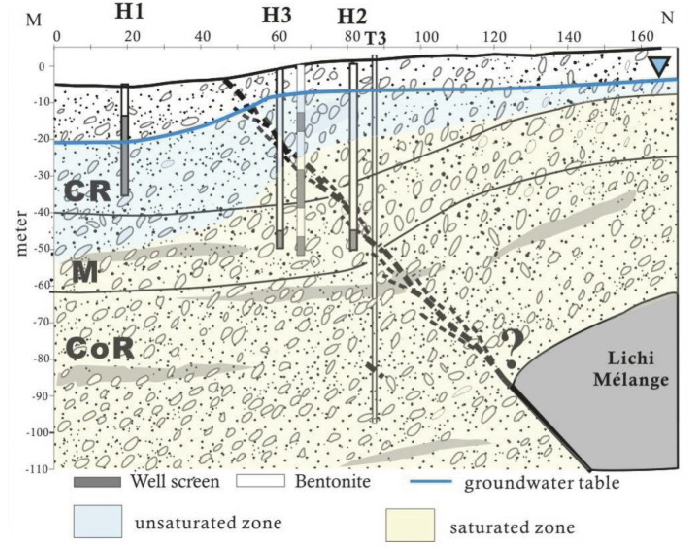
斷層帶地下水文模式Hydraulic system across the fault

圖二、利用本實驗場之5口地下水井進行抽注水試驗及定期微水試驗,進而得到斷層帶地下水文模型。
|


